Lesson Plan: Advantages and Possible Negative Impacts of Using Genetic Engineering in Arable Farming
Abstract
This lesson plan is designed to guide students in enquiring the multifaceted implications of genetic engineering in arable farming. It demonstrates how teacher can facilitate students’ geographical understanding of the spatial interactions between the physical environment and human society using inquiry-based learning and assessment for learning strategies under the topic of addressing food issues at local and National scales. At the same time, this plan also aims to smoothen the transition of geography learning between low forms and senior forms. Besides preparing students with concrete understanding of geographical concepts, interactive in-class activities are designed to promote students’ critical-thinking skills necessary for the 21st century.
Background
One of the key natures of geography that distinguishes it from other subjects, refers to its inquiry into spatial interaction between the physical environment and human society. According to the Geography Curriculum and Assessment Guide (EDB, 2017), famine problem refers to students’ understanding of food problems on a global scale. Genetic engineering as one of the scientific engineering methods in solving food problems in the world brings both benefits and negative impacts to the sustainability of agriculture. This reveals the requirement of preparing students with critical-thinking skills to live in the new era of the 21st century.
Topic: What are the advantages and possible negative impacts of using genetic engineering in arable farming?
Previous Knowledge
Students should be familiar with:
- Spatial distribution of major natural hazards affecting farming in China.
- Components and processes of the farming system (input, farming process [ploughing, irrigating, fertilizing, harvesting], output).
- Possible directions to solve farming problems in China: improve the farming condition of land, improve the crop seeds, and improve farming efficiency.
Learning Objectives
Knowledge:
- State the key purpose of using genetic engineering in farming.
- List the advantages that pest-resistant genetically-modified (GM) crops have on arable farming in China.
- List the possible negative impacts genetically-modified (GM) crops have on farming in China.
Skills:
- Extract information from reading materials to learn about China’s policy on planting and importing GM crops.
- Interpret data on China’s demand and production of crops from the table.
Attitude:
- Show concern for impacts caused by genetic engineering on food safety and the natural environment.
Learning Problems/Needs Identified from the Previous Lesson
- Students found it difficult to understand how the planting of GM crops negatively affects the environment.
- Students reflected unfamiliarity with China's context.
- Students are unfamiliar with poster design, which requires longer time to complete the work.
- Students are not familiar with geography terms in English.
Before going deep into discussing or evaluating the “possible environmental, economic and social implications of genetically modified food” of a specific location in senior forms, the basic concepts of “what genetic engineering is” and “merits and demerits of genetic engineering” should be first constructed in low forms (EDB, 2011; EDB, 2017). Therefore, a life-related inquiry scenario is provided to inspire students to think about the benefits and concerns brought by genetic engineering techniques in daily food consumption.
Lesson Outline
Stage 1: Introduction: Life-based scenario input- a domestic cuisine (5 minutes)
Purpose: Activate previous knowledge and introduce the lesson objectives.
Teaching Steps:
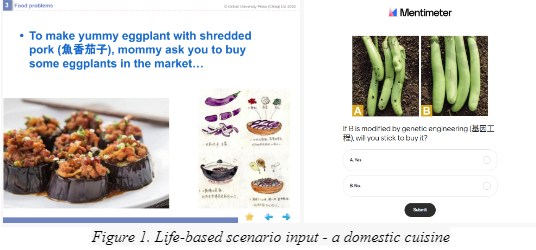
- Introduce the outline of the lesson using PPT slides (Figure 1.1).
- Engage students with a question on which set of eggplants they would choose and why using Mentimeter (Figure 1.2).
Student Activities:
- Identifying features from photos.
- Voting on Mentimeter and discussing choices.
Resources: PPT, Mentimeter
Assessment: Questioning, Poll on Mentimeter
On the other hand, Assessment for Learning strategies are applied to support students learning progress.
To facilitate students’ learning by inquiring and giving timely and concrete feedback based on students’ learning performances at different stages of the lesson, A set of inquiries is designed to support students in building a comprehensive understanding of the impacts and limitations of genetic modification technology related to the daily life in a logical way.
“What is genetic engineering? What’s the main purpose of using genetic engineering in farming?”
“What are the advantages of GM crops in farming? Though with a higher yield, why are there still restrictions for growing and selling GM crops?”
“What are the possible negative impacts of genetic engineering on the sustainability of agriculture?”
“Should we buy GM food? Under what condition may you buy GM food?”
To support effective questioning, various types of assessment tasks (e.g. votes, multi-choice questions, discussion word cloud) are designed to check students’ learning performance and facilitate their learning progress. However, as the paper worksheet has a problem of delayed feedback, e-assessment apps like Mentimeter are used to display the overall results of the respondents from the classroom synchronically, which supports teachers in adjusting the teaching process accordingly.
Stage 2: Key Knowledge and Skills Development (21 minutes)
Purpose: Teach the core content and develop key skills.
Part 1: Key Purpose of Genetic Engineering (5 minutes)
Teaching Steps:
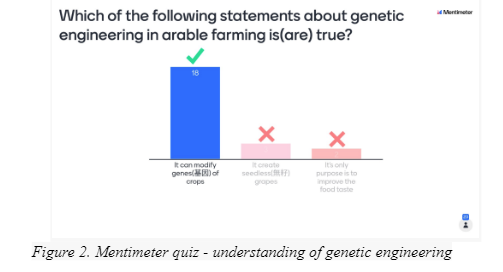
Use Mentimeter quiz to check understanding of genetic engineering (Figure 2).
Guide students to discover the main purpose of genetic engineering through PPT slides (Figure 3).

Student Activities:
- Complete Mentimeter Quiz.
- Answer questions in class.
Resources: PPT, Mentimeter
Assessment: Questioning, Mentimeter Quiz
Part 2: Advantages of Pest-Resistant GM Crops (4 minutes)
Teaching Steps:
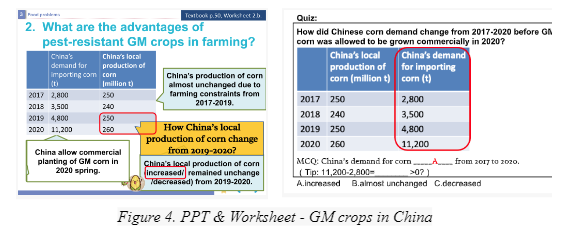
- Discuss advantages using PPT slide (Figure 4.1) and worksheet.
- Summarize change in China's corn production using PPT slide.
Student Activities:
- Read materials and complete worksheet (Figure 4.2).
- Answer questions in class.
Resources: PPT (slides 9-10), Worksheet
Assessment: Questioning, Worksheet completion
Part 3: China’s Policy on GM Crops (4 minutes)
Teaching Steps:
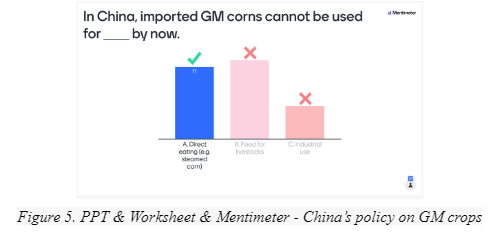
- Summarize China’s policy on GM crops using PPT slide (Figure 5.1).
- Discuss causes for restrictions on GM crops using PPT slide (Figure 5.1).
Student Activities:
- Interpret data in reading materials (Figure 5.2).
- Answer questions in class.
Resources: PPT (Figure 5.1), Mentimeter (Figure 5.3)
Assessment: Questioning, Worksheet completion (Figure 5.2)

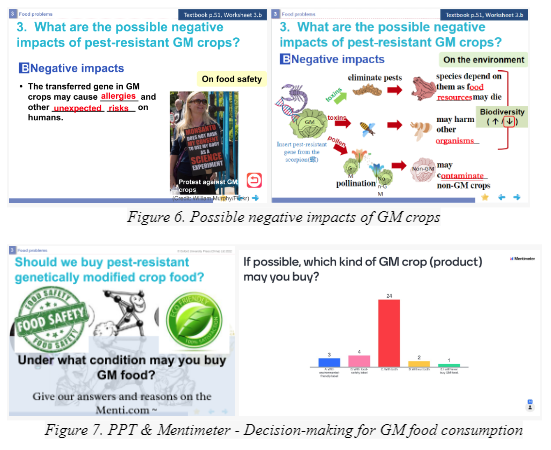
Part 4: Exploring Negative Impacts (8 minutes)
Purpose: Understand the possible negative impacts of GM crops.
Teaching Steps:
- Discuss the negative impacts on food safety and the environment using PPT slides (Figure 6).
Student Activities:
- Participate in discussions on food safety and environmental impacts.
- Decision-marking for GM food consumption (Figure 7)
Resources: PPT, Mentimeter
Assessment: Questioning, Mentimeter Poll
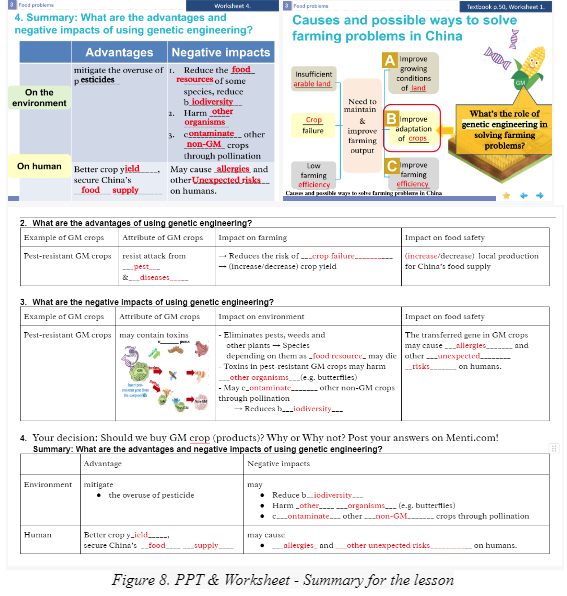
At the same time, a paper worksheet containing a summary table is provided to help students record ideas in steps and finally construct the whole image of the “purpose - advantages & possible negative impacts - decision marking” related to genetic engineering at the end of the lesson.
Stage 3: Summary and Conclusion (3 minutes)
Purpose: Recap key points and address any remaining questions.
Teaching Steps:
- Summarize the lesson’s key points.
- Address any remaining student questions.
Student Activities:
- Participate in summary discussion.
Resources: PPT slides
Assessment: Questioning
Resources
- PowerPoint slides (Figure 8.1)
Worksheet (Figure 8.2)
Conclusion
- This lesson plan outlines a structured approach to teaching the advantages and possible negative impacts of using genetic engineering in arable farming. Through a combination of interactive activities, discussions, and assessments, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of the topic and develop critical thinking skills related to food safety and environmental impacts at low form. It helps to prepare students with detailed and precise explanation and elaboration skills in essay writing in the senior forms.
References
- Education Bureau HKSARG. (2011). Geography Curriculum Guide (Secondary 1-3).
- Education Bureau HKSARG. (2017). Geography Curriculum and Assessment Guide (Secondary 4-6).